The Golden Triangle of Screening: Why the 3-Site MRSA Swab is Essential for Your Health
In the fight against MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), knowledge is the first line of defense. While we know that testing is important, many people ask: Why is the MRSA swab taken from multiple sites, and is one site enough?
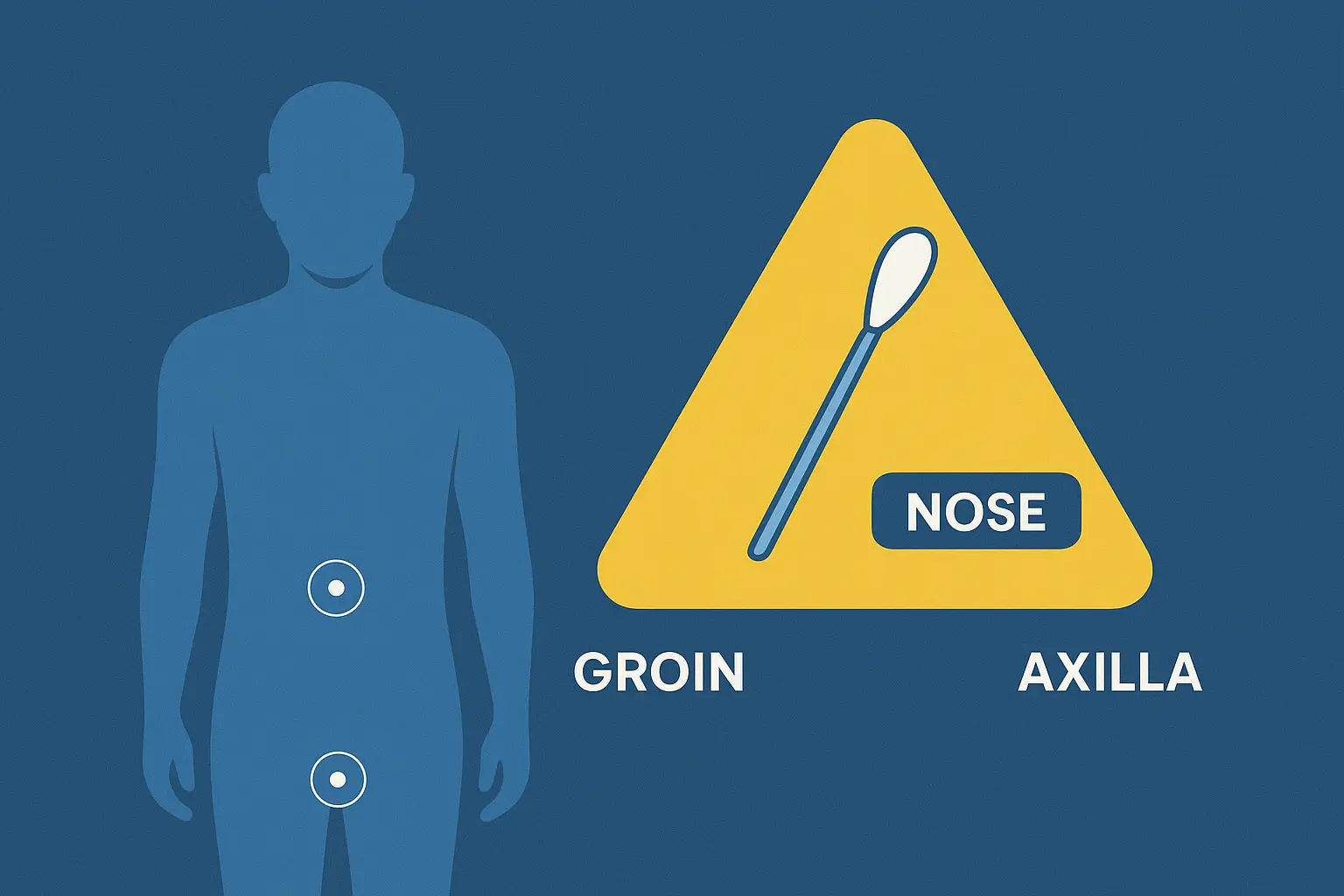
The answer lies in maximizing detection and minimizing risk. The standard MRSA screening procedure focuses on what we call the “Golden Triangle of Screening”: the nose, the groin, and the armpit (axilla). Using this MRSA multi-site screen is not arbitrary—it’s medically essential.
Why is MRSA Screening So Important?
As we’ve discussed, the biggest threat from MRSA comes from colonization. This means you are an MRSA carrier—you host the bacteria, but you show no MRSA symptoms.
However, being colonized puts you and those around you at risk, especially in healthcare settings.
- Preventing Infections: If you are colonized and undergo surgery, the bacteria can transfer from your skin to the surgical site, causing a serious, life-threatening MRSA infection.
- Stopping the Spread: Carriers can easily spread the bacteria to vulnerable individuals in hospitals or care homes. MRSA screening allows doctors to implement decolonization protocols before the bacteria can cause harm.
The Golden Triangle: Why We Swab Three Sites
The bacteria doesn’t always reside in one place. Relying solely on a nasal swab significantly lowers your chances of finding a colonized individual. For the highest MRSA test accuracy, samples are collected from the three most common MRSA colonization sites:
1. The Nasal Swab (The Most Common Site)
The interior of the nose is the primary MRSA carrier reservoir. Many screening programs historically started and ended here.
2. The Groin Swab (The Hidden Reservoir)
The groin area is frequently colonized, particularly in hospitalized or long-term care patients. Studies have repeatedly shown that many carriers who test negative on a nasal swab alone will test positive when a groin swab is included.
3. The Axilla Swab (The Sensitivity Booster)
The axilla (underarm) is an additional colonization site. Including this third site is critical because it significantly increases MRSA detection rates. Research shows that combining samples from the nose and groin alone offers up to 98% sensitivity, and including the axilla further solidifies that accuracy.
The takeaway is clear: If you only test one site, you risk a false negative, meaning you might be an MRSA carrier without knowing it. A multi-site approach provides the confidence and accuracy required for effective prevention.
How the Multi-Site MRSA Swab Test Works
Whether you choose a standard MRSA culture test (results in 24–72 hours) or an MRSA PCR rapid test (results in hours), the collection method using our MRSA swab collection kit is simple:
- Collection: Using the supplied swab, you gently collect samples from the designated three sites (or two, depending on the kit variation you choose).
- Lab Analysis: The sample is sent to the lab for analysis. For the fastest results, the PCR test uses molecular technology to detect the bacteria’s genetic material instantly, offering unparalleled speed for urgent pre-surgery MRSA test needs.
Knowing your colonization status is the first step toward taking control of your health and protecting those around you.
Don’t Guess, Test Accurately.
If you are scheduled for surgery, work in healthcare, or simply need assurance, relying on the highest MRSA test accuracy is non-negotiable. Choose a multi-site screen for maximum peace of mind.
[🛒 Click Here to Explore Our MRSA Multi-Site Screening Kits Today]