HbA1c Blood Test: A Complete Guide to Understanding Your Results
If your doctor has recommended an HbA1c blood test, it’s completely normal to feel a mix of confusion and concern. You may be asking yourself: what exactly is ‘glycated haemoglobin’? How is this different from a standard finger-prick glucose check? And most importantly, what do the numbers on my test result actually mean for my health? The medical jargon alone can be intimidating, leaving you feeling unsure of where you stand and what to expect.
This guide is here to provide clear, reassuring answers. We will demystify this vital health check, explaining in simple terms what it measures and why it provides a crucial three-month overview of your average blood sugar levels. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge to read your results with confidence, understand their implications for diabetes management, and feel fully prepared for a productive conversation with your GP. Let’s take the first step towards gaining control and clarity over your health monitoring.
What Is an HbA1c Test? A Simple Explanation
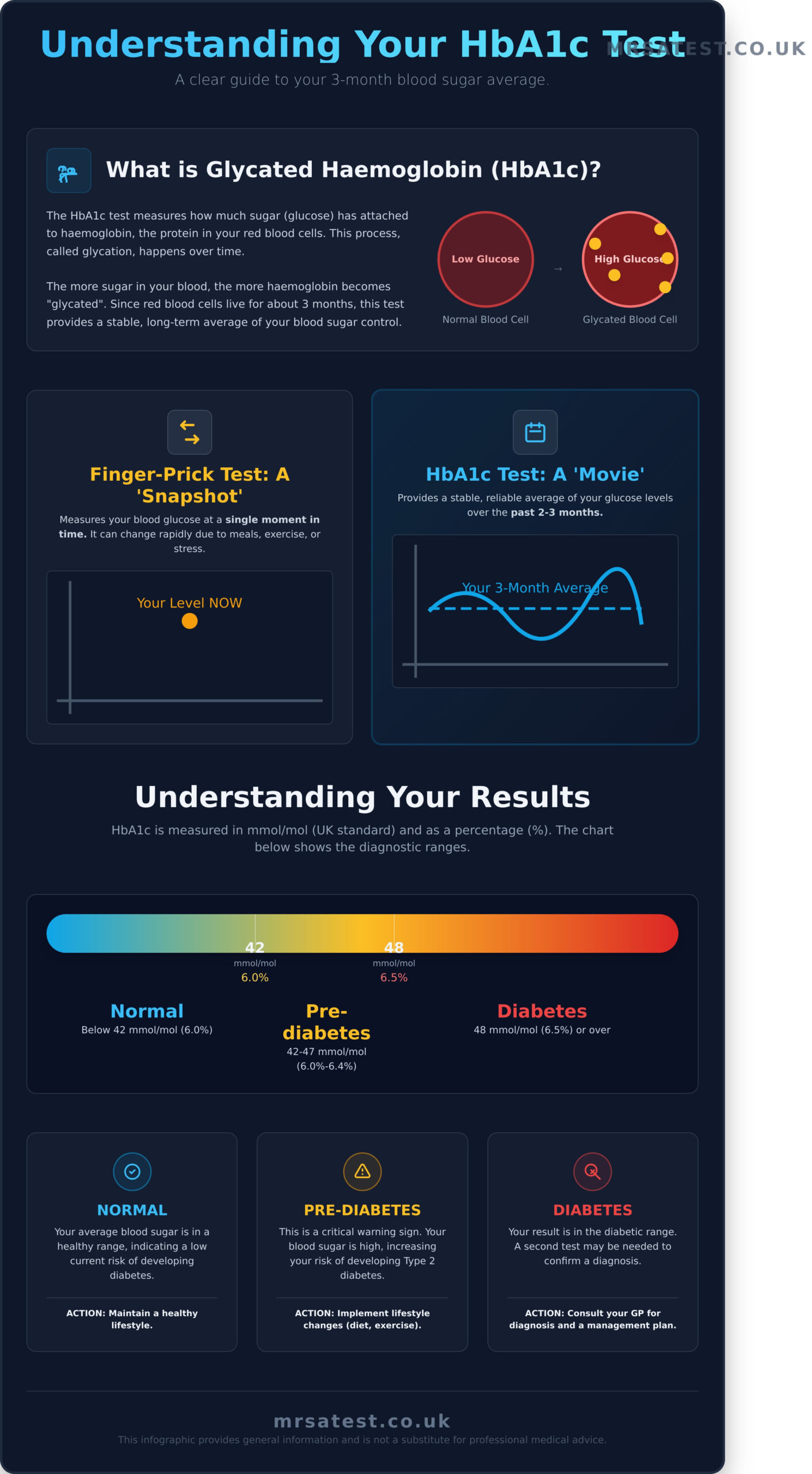
The hba1c blood test is a simple and crucial diagnostic tool that provides a reliable overview of your average blood sugar (glucose) levels over the previous two to three months. Unlike a daily glucose check, it isn’t affected by short-term changes from a recent meal or exercise. Think of it this way: as sugar travels through your bloodstream, some of it naturally sticks to your red blood cells, a bit like honey coating a spoon. This test measures how much sugar has attached, giving your doctor a clear, long-term picture of your blood sugar control.
Demystifying ‘Glycated Haemoglobin’ (HbA1c)
To understand the test, it helps to know what haemoglobin is. Haemoglobin is the protein inside your red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout your body. When glucose levels in your blood are high, sugar molecules permanently bind to this protein. This process creates what is known as Glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c). The more glucose in your blood over time, the more haemoglobin becomes ‘glycated’. The result of an hba1c blood test is given as a percentage, representing the proportion of your red blood cells that are coated with sugar.
The 3-Month Average: A ‘Movie’ of Your Blood Sugar, Not a ‘Snapshot’
A standard finger-prick glucose test provides a ‘snapshot’-it tells you your blood sugar level at that exact moment. While useful for daily management, it can fluctuate significantly based on what you’ve just eaten, your stress levels, or recent activity. In contrast, the HbA1c test is like watching a ‘feature film’ of your blood sugar over the last 2-3 months. This is because red blood cells have a lifespan of about three months. By measuring the sugar attached to them, your doctor gets a stable and comprehensive average, which is far more reliable for diagnosing and monitoring conditions like diabetes and pre-diabetes.
Why Is the HbA1c Test Performed?
A doctor will order an hba1c blood test for several key reasons, primarily because it offers a reliable, long-term overview of your blood sugar levels. Unlike a traditional blood glucose test which provides a snapshot of a single moment, the HbA1c test reflects your average glucose levels over the preceding two to three months. This comprehensive view makes it an invaluable tool for diagnosing, monitoring, and managing diabetes and pre-diabetes.
Diagnosing Type 2 Diabetes and Pre-diabetes
The HbA1c test is considered a gold standard for diagnosing Type 2 diabetes. A high result indicates that your blood sugar has been consistently elevated, a clear sign of the condition. One of its main advantages is convenience, as it does not require you to fast before the blood sample is taken. The test is also crucial for identifying pre-diabetes, a critical warning stage where blood sugar is high but not yet in the diabetic range. According to trusted resources like MedlinePlus, the Hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) Test helps pinpoint this risk, allowing for early lifestyle interventions that can prevent or delay the onset of full diabetes. It is important to note, however, that this test is not the primary method for diagnosing Type 1 diabetes, which often develops rapidly and requires different immediate tests.
Monitoring Long-Term Glucose Control
For individuals already living with diabetes, the hba1c blood test is an essential component of their ongoing care. It provides a clear and accurate picture of how well their diabetes is being managed over time. Regular testing helps patients and their healthcare providers assess the effectiveness of treatment plans and make necessary adjustments.
Specifically, doctors use the results to:
- Set personalised HbA1c targets: Establish a goal for blood sugar control tailored to the individual.
- Evaluate treatment effectiveness: Determine if current medications, diet, and exercise are successfully managing glucose levels.
- Adjust care plans: Make informed decisions about changing medication dosages or recommending lifestyle modifications.
- Reduce complication risks: Consistent monitoring helps minimise the risk of long-term diabetes complications, such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and heart conditions.
Most people with diabetes will have this test performed every 3 to 6 months. This regular assessment is fundamental to maintaining good health and preventing the serious consequences of poorly controlled blood sugar.
Understanding Your HbA1c Results: The Numbers Explained
Once you receive the results of your hba1c blood test, you will see a number given in mmol/mol (millimoles per mole), which is the standard unit in the UK. You may also see it expressed as a percentage (%). This figure represents your average blood glucose level over the past two to three months and helps to identify your risk of diabetes.
It is important to remember that the ranges below are general guidelines for diagnosis. Your personal target may differ based on your age, overall health, and other medical conditions. Always discuss your specific results with your GP for an accurate interpretation and personalised advice.
HbA1c Results Chart: Normal, Pre-diabetes, and Diabetes
The diagnostic thresholds are clearly defined to categorise your result into one of three ranges:
- Normal: Below 42 mmol/mol (below 6.0%).
- Pre-diabetes: 42 to 47 mmol/mol (6.0% to 6.4%). This range indicates a high risk of developing diabetes.
- Diabetes: 48 mmol/mol (6.5%) or over. A result in this range on two separate occasions can confirm a diagnosis.
What Your Result Means for You
Understanding where your number falls on this scale is the first step towards managing your health effectively.
- A normal result indicates that your blood sugar levels have been within a healthy range, signifying a low current risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- A result in the pre-diabetes range is a crucial warning sign. It means your blood glucose is higher than it should be and acts as a call to action. With proactive lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, it is often possible to lower your HbA1c and prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
- Receiving a result in the diabetes range means it is essential to consult your GP. This result is a key factor in the clinical diagnosis of diabetes, and your doctor will work with you to create a comprehensive management plan. This plan will focus on controlling your blood sugar levels to reduce the risk of long-term health complications.
No matter the outcome of your hba1c blood test, the result provides valuable information. It empowers you and your healthcare provider to make informed decisions about your future health.
Preparing for the Test and Factors That Can Affect Accuracy
Understanding what to expect before, during, and after your test can help alleviate any concerns. The good news is that an HbA1c blood test is a simple and routine procedure that requires very little special preparation. However, being aware of certain factors that can influence the result is key to ensuring you and your doctor have the most accurate picture of your health.
How to Prepare for Your HbA1c Test
One of the primary benefits of this test is its convenience. Unlike many other blood tests used to check glucose levels, you do not need to fast. You can eat and drink as you normally would right up to your appointment. You should also continue to take any regular medications unless your GP or nurse has specifically instructed you otherwise. For a smooth and quick blood draw, it is helpful to wear clothing with sleeves that can be easily rolled up.
What to Expect During the Blood Draw
The process is a standard blood draw that is typically completed in just a few minutes by a nurse or phlebotomist. A tourniquet (a tight band) will be placed around your upper arm to make the vein more prominent. The professional will then clean the area with an antiseptic wipe before gently inserting a sterile needle. A small sample of blood is collected into a vial, the needle is removed, and a small plaster or cotton pad is applied to the site to stop any bleeding.
Conditions That Can Influence Your HbA1c Reading
While highly reliable for most individuals, certain health conditions can affect the accuracy of an hba1c blood test. This is primarily because the test measures glucose attached to red blood cells, and anything that alters the lifespan of these cells can skew the result. It is vital to discuss your full medical history with your doctor. Key factors include:
- Anaemias: Conditions like iron-deficiency anaemia, sickle cell anaemia, or thalassaemia can lead to falsely high or low results.
- Kidney and Liver Disease: Severe or end-stage kidney or liver disease can interfere with the test’s accuracy.
- Recent Blood Loss or Transfusion: A recent, significant bleed or having received a blood transfusion will affect the average age of your red blood cells and, therefore, the result.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal and physiological changes during pregnancy can also impact readings.
Informing your healthcare provider of these conditions allows them to interpret your results in the correct context, ensuring you receive the most appropriate care and advice.
Next Steps After Receiving Your HbA1c Results
Receiving the results of any medical test can feel overwhelming, but it is essential to view the outcome as a data point, not a final judgment. Your hba1c blood test result is an important piece of information that provides a valuable insight into your average blood sugar levels over the past few months. The most critical action you can take now is to discuss this result with a qualified healthcare professional. This step is not just a formality; it is the key to understanding what the number means for your personal health and creating a clear path forward.
Why You Must Discuss Your Results With a Doctor
An HbA1c result cannot be accurately interpreted in isolation. Your GP will assess the number in the full context of your individual health profile, including your age, weight, family history, and any existing medical conditions. They are trained to confirm a diagnosis, which often requires a repeat test to ensure accuracy, and to rule out other factors that can influence HbA1c levels, such as certain types of anaemia or kidney issues. This comprehensive medical consultation ensures you receive a precise diagnosis and appropriate guidance.
Key Questions to Ask Your GP
To make your consultation as productive as possible, it helps to be prepared. Having a list of questions ready can empower you to take an active role in managing your health. Consider asking your GP the following:
- What does this result mean for me specifically, considering my personal health history?
- What are the next steps? Do I need a repeat test or any other diagnostic checks?
- What specific lifestyle changes, such as diet and physical activity, do you recommend I start with?
- Is medication necessary at this stage? If so, what are the options and their potential side effects?
- How often should I be re-tested to monitor my progress and manage my health effectively?
- Are there any local NHS services or support groups you would recommend?
Your GP is your partner in health. This conversation is the starting point for developing a manageable and effective plan to protect your long-term wellbeing. By understanding your hba1c blood test result and the actions you can take, you are putting yourself in control of your health journey.
Your Path Forward: Key Takeaways on the HbA1c Test
Understanding your health is the first step to taking control of it. As we’ve covered, the HbA1c test provides a crucial long-term perspective on your average blood sugar, offering a much clearer picture than a single daily reading. Your results are a key indicator for diagnosing prediabetes, managing diabetes, and assessing your overall metabolic health. Think of the hba1c blood test not as a final verdict, but as a valuable piece of information to guide your next steps and facilitate an informed discussion with your GP.
Navigating medical information requires a source you can trust. At mrsatest.co.uk, we are committed to providing that security. We stand by our commitment to accuracy and confidentiality, with all tests processed in a trusted UKAS-accredited laboratory. This ensures you receive clear, dependable results that empower you to make confident decisions about your health and wellbeing.
Knowledge is power, especially when it comes to your health. To continue building your understanding, explore our health articles for trusted, clear information. You’ve already taken an important step by seeking knowledge, and that is a foundation for a healthier tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between an HbA1c test and a finger-prick blood sugar test?
A finger-prick blood sugar test provides a “snapshot” of your glucose level at a single moment in time. It measures the amount of sugar currently in your bloodstream. In contrast, the HbA1c test offers a long-term view, reflecting your average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. It measures how much glucose has attached to your red blood cells, providing a more stable and comprehensive picture of your blood sugar control over time.
How often should I have my HbA1c level checked?
The recommended frequency depends on your individual health status. If you have been diagnosed with diabetes, the NHS typically advises an HbA1c check every 3-6 months until your levels are stable, and then at least annually thereafter. For those identified as being at high risk of developing diabetes (prediabetes), a yearly check is often recommended. Your GP will provide a personalised testing schedule based on your specific circumstances and treatment plan.
Can my HbA1c level be lowered?
Yes, it is possible to lower your HbA1c level through proactive management. Consistent lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a balanced diet low in processed sugars, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight, are highly effective. For some individuals, medication prescribed by a doctor may also be required to achieve target levels. These combined efforts can significantly improve your long-term blood sugar control and reduce your HbA1c reading.
Is the HbA1c test accurate for everyone?
While the HbA1c test is highly reliable for most people, certain medical conditions can affect its accuracy. Conditions that impact red blood cells, such as sickle cell disease, thalassaemia, or severe iron-deficiency anaemia, can lead to misleading results. The test may also be less reliable if you have chronic kidney or liver disease or have recently had a blood transfusion. It is crucial to discuss your full medical history with your GP to determine if the hba1c blood test is appropriate for you.
Can the HbA1c test be used to diagnose Type 1 diabetes?
The HbA1c test is not the preferred method for diagnosing Type 1 diabetes. This is because Type 1 diabetes can develop very rapidly, and the HbA1c test reflects an average over two to three months, potentially missing a sudden, sharp rise in blood glucose. Diagnosis of Type 1 diabetes usually relies on measuring current blood glucose levels and testing for specific autoantibodies. A GP will determine the most suitable diagnostic tests based on your symptoms.
Does a high HbA1c level always mean I have diabetes?
A high HbA1c level is a key indicator, but it does not automatically confirm a diabetes diagnosis on its own. An HbA1c result in the prediabetes range (42-47 mmol/mol) signals a high risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. As other factors can influence the result, a healthcare professional will consider your symptoms and may order a repeat test to confirm the diagnosis. A confirmed result of 48 mmol/mol or above typically leads to a diagnosis of diabetes.